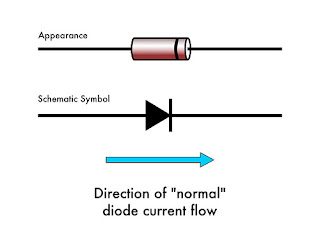
To understand how Zener diodes are different from other diodes, let’s first review the properties of regular diodes. And, while there are many different types of diodes– see herefor a long list –we’re going to focus on so-called “normal” semiconductor diodes, most commonly constructed with a p-n silicon junction.Diodes usually come in glass or plastic cylindrical packages, marked with a stripe on one side to indicate polarity. In a perfectly ideal diode, current flows in one direction only, from the anode (positive side) to the cathode (negative side) which is marked with the stripe. The schematic symbol is a triangle pointing towards a bar, where the current flows in the same direction, towards the barred (striped) end. Surface mount versions of diodes tend to follow the same labeling convention, where the cathode end is marked with a broad stripe.